Modern computers are quite complex devices, which require that all their components fit together and work in maximum symbiosis.
If you want to build a powerful machine, you need to take care that all the equipment has good parameters of work and fit together. This is especially important when e.g. choosing a motherboard.
Another important choice for the stability of your PC will be a good HDD. For this reason, it will be responsible for all the data stored on your computer, and including the speed of reading and writing hard drive will directly affect the stability of the entire system.
What is a HDD
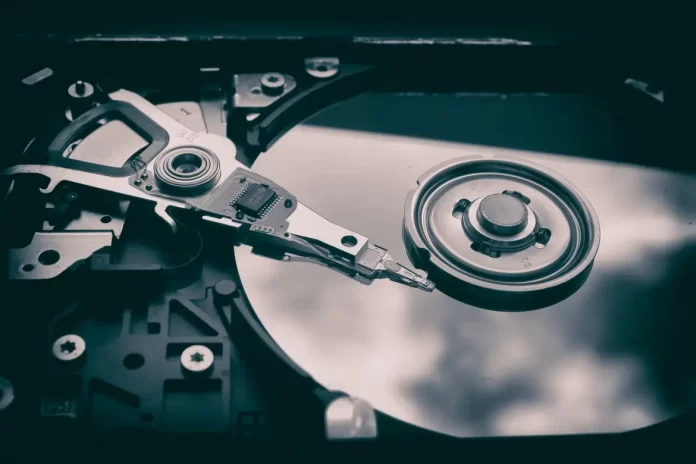
A HDD is a hard disk drive or just a hard disk. It’s a random access storage device based on magnetic recording technology. It’s currently the most popular storage device on most computers.
Information is recorded on the hard drive’s wafers, typically made of glass or aluminum and coated with a ferromagnetic material, usually chromium dioxide. This makes them magnetic disks. Hard disks usually use one or more of these platters.
The read head in such disks doesn’t touch the surface of the platters and a few nanometers remain between them. The absence of mechanical contact, in this case, ensures a long life of these devices.
Solid-state SSDs are becoming increasingly popular. They have much faster data transfer rates and are more compact in size. However, they have fewer write cycles than a HDD and will therefore fail more quickly.
What Factors Affect the Speed of Your HDD
The read speed of a hard drive is directly related to the rotation speed of the internal spindle. It’s generally accepted that the gold standard for hard drive spindle speed is 7200 RPM.
Models with higher speeds are usually used in server installations. They will be faster, but in this case, the energy consumption and heat dissipation will also be much higher.
In addition, the spindle head has to move to a certain area of the disk when reading information. This results in a small delay, which also affects the reading speed. It’s measured in milliseconds and usually, the optimal delay should be between 7-14 ms.
Another parameter that affects the speed of your hard disk drive is the cache size. The size of the cache also has an effect on this parameter. The fact is that when data is accessed for the first time, it’s placed in temporary storage called a buffer. The greater the volume of this storage, the more information can be stored there, and accordingly, its subsequent reading will be several times faster.
Usually in popular models cache volume is set in the range of 8-128 MB. This is more than enough for normal daily use.
Read speed also varies with the amount of data on the drive and is directly related to the placement of the tracks on the drive. The more data there is, the slower it’s to get to the right sector, and files are more likely to be written to different clusters, which will also affect read performance.
The speed is also affected by the type of file system your hard drive runs on. The most commonly used file systems are NTFS and FAT32. NTFS is more susceptible to fragmentation in system-specific areas, so the disk heads make more movements than when FAT32 is installed. Hence we can conclude that FAT file systems are generally faster than NTFS.
The last thing that may affect the speed of your HDD is the version of the SATA connection interface. First-generation SATA has a bandwidth of 1.5 GB/s and SATA 2 has a bandwidth of 3 GB/s, which can also affect the performance and cause some performance limitations if you use modern drives on older motherboards.
What are the write speed specs for hard drives
When we’re talking about write and read speeds, it’s worth remembering that it depends on the size of the files you want to read. Files over 500 MB should read at 150 MB/sec, then it’s considered more than acceptable. System files usually don’t take up more than 8 KB of disk space, so an acceptable read rate for them is 1 MB/s.
How to check the speed of your hard drive
You can check the read and write speed of your HDD, USB thumb drive, or SD memory card with the built-in WinSAT utility, which is already present by default in Windows Vista, 7, 8, and 10.
It’s pretty easy to do and all you need to do is:
- In Windows, click the “Start” button.
- After that, in the list of programs, find the “Utilities – Windows” section and in it the “Command Prompt” item.
- Then right-click on it and select “Advanced > Run as administrator” in the context menu and confirm the action.
- To start the program you simply need to type in the command winsat disk and click on Enter
The results of the speed tests will be displayed in the console window. Then you need the following lines
- Disk Random 16.0 Read – read speed of random 256 blocks of 16KB (i.e. 4MB of test data);
- Disk Sequential 64.0 Read – read speed of sequential 256 blocks of 64 KB size (16 MB of test data);
- Disk Sequential 64.0 Write – write speed of sequential 256 blocks of 64 Kb size (16 Mb of test data).
In addition, next to the test results you will see the performance index of your hard drives. For Windows 7 it ranges from 1.0 to 7.9, and for Windows 8 and 10 it ranges from 1.0 to 9.9.
This way you can quickly and easily check the performance of your hard drives