As you probably know or have heard – a computer understands only information about zeros and ones. Something like Morse, but on a much more global scale. That is why certain kinds of network cables are used to transmit information. Why precisely network – the fact that the connection of a computer with another similar device or another computer can already be called a network.
At the moment the Internet network is used by a huge number of people, which is connected to a lot of computers, laptops, phones, servers, switches, routers, and other network devices. Network cables are used to interconnect multiple computers or servers. Even now you’re reading this article and the signal passes through thousands of such wires and reaches you.
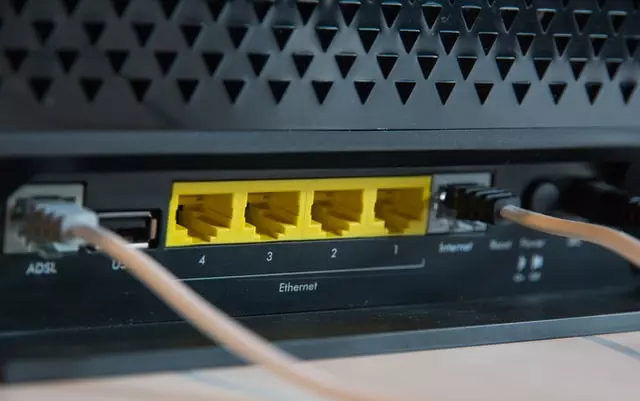
What is an Ethernet cable
The Ethernet cable is used to transmit digital or analog information. Depending on the application, the twisted-pair cable differs in electrical and mechanical parameters. To understand and determine what kind of cable you need, let’s look at the technical and physical differences in the categories of Ethernet cables.
Twisted pair cable categories are classified in the EIA/TIA-568 specification and in the international standard ISO 11801. There are many types (UTP, FTP, STP, S/FTP, SFTP) with different numbers of conductors (1 pair – 2 conductors … 500 pairs – 1000 conductors), which in turn are divided into categories based on different specifications. The category of the cable determines in what conditions it can be used. When organizing small networks at home or in the office the category of network cable can not even think about, because at small distances and speeds, this question isn’t relevant.
Networks can be made from almost any cable, plug, and socket. To connect a user to the Internet, as well as to create a local computer network is usually used UTP 2 or 4 pairs, category 5 and 5e. For analog telephony is used twisted-pair UTP category 3 and below, but sometimes used 5. What are the differences between cable specifications, and how do choose the right category, use unshielded, shielded, twisted, or solid – let’s try to understand this.
Read Also:
- What is a PoE switch
- What is WAN Miniport
- What is the difference between Ethernet Splitter and Switch?
What kinds of Ethernet Cable are there
There are three types of cable for the Internet: coaxial, fiber optic, and twisted pair.
Twisted pair is a network cable suitable for local area networks. It consists of two or four twisted pairs of wires. Every two wires connected in pairs are only used to send or receive a signal. The principle of twisted pair is to connect two nodes and use separated media to transmit data in different directions. Twisted pair connects equipment up to 100 meters away in a single network. Because of its low cost and ease of use, it is increasingly being chosen to form Local Area Networks (LAN) and to carry the Internet indoors.
Fiber optics is the fastest way to transmit information today. Among its advantages:
- High bandwidth;
- Long service life;
- Rapid detection of unauthorized connections, which makes the network more secure;
- High noise reduction, good protection against interference;
- Fast data transfer.
Fiber-optic network wires use the method of transmitting light rays using total internal reflection. An important advantage of such a cable for connecting to the Internet is the lack of restrictions on the length of the backbone. That is why it can connect significantly distant objects. Although fiber optic itself is inexpensive, the equipment for it has a very high price.
Coaxial cable – This type is used in security alarms, video surveillance, and television. Its working principle is the transmission of radio-frequency electrical signals, and the signal strength is closely related to the length of the backbone and the distance to which it will be sent. Coaxial cable can be thin and thick. The diameter of the former (category RG-58/U) is up to 0.5 cm. It’s highly flexible, but the signal transmitted through it fades quickly. It can be used to send data over short distances, the maximum speed is up to 10 Mbit/s. The diameter of the thick cable is 1 cm. It has increased rigidity and is mounted with expensive equipment.
What about Ethernet cable categories
Of all types of network cables for the Internet in an apartment, office, or house, it’s best to choose twisted-pair category 5E. When buying, you need to pay attention to a number of criteria, otherwise, a bad wire will cause a weak signal and constant loss of connection, which plays especial role for gamers. There are a total of 7 categories of wire:
- Categories 1, 2, and 4 are almost never used. Type 3 is chosen for telephone lines.
- Categories 5 and 5e have almost no differences, the fifth is actually on sale. Since 2010, after the emergence of 5E, manufacturers, almost without changing the Internet cable, began to put this category on the sheath. It’s the most popular today.
- Category 5E cable is a 2-pair (4-core) or 4-pair (8-core) cable with data rates of up to 100 and 1000 Mbps. Also, a four-pair cable is laid for networks with speeds of 1 Gbit / s. The maximum allowable distance for it is 100 meters.
- Category 6 consists of four pairs and is designed for networks up to 10 Gbit/s. For speeds up to 1 Gbit/s, the maximum wire length is 100 meters, with speeds up to 10 Gbit/s – 55 meters.
- Categories 6a, 7 and 7a have shielded cables for networks up to 10 Gbit/s and backbones up to 100 meters. Application of such shielding means higher requirements for equipment and installation (good grounding is necessary), that’s why most often such wire is preferred to use fiber optic.
| Category (CAT) | Frequency, MHz | Signal rate, Mbit/s |
| 5 | 1-100 | 10,100 |
| 5e | 1-100 | 10, 100, 1 Gbit/s (eight-core cable) |
| 6 | 1-250 | 10, 100, 1 Gbps |
| 6a | 1-500 | 10, 100, 1 Gbit/s, 10 Gbit/s |
| 7 | 1-600 | 10, 100, 1 Gbit/s, 10 Gbit/s |
| 7a | 1-1000 | 10, 100, 1 Gbit/s, 10 Gbit/s |
Keep in mind that the category only tells you the quality of the Internet cable. It’s mistakenly thought that changing the wire will change the frequency at which it operates. This is incorrect. The cable operates at the frequency of the network equipment. Replacing a high-quality category five with a category six won’t increase the speed of the signal or the condition of the connection.
Is connecting via fiber-optic cable the best solution
Fiber optic for home and office is expensive due to the equipment, it’s unreasonable to use it as a wire for a local network. The main advantage – a significant speed of information transfer – doesn’t justify the cost, since a few computers are not able to create the kind of traffic for which it is designed. Fiber optics is used for Internet connection to populated areas or multi-story houses. It’s not afraid of line interference and long distances, so it is well suited for such tasks.
Most well-known providers have already upgraded their own lines and use fiber optics and the appropriate equipment to connect users. This is more convenient for a number of reasons:
- Good bandwidth;
- A greater length of trunks without degradation of signal quality;
- Space-saving in the CRT cabinets.
Some providers offer the introduction of fiber optic in the room, which provides a stable signal of high quality. But even with the introduction of fiber optic in the apartment wiring inside is better to do with twisted pair. It is cheaper and easier to install. Fiber optic wire is fragile and afraid of kinks. If it’s damaged, the signal will be lost. For these reasons, a special fiber optic cable is introduced into the apartment or house and connected to the converter, and from the latter, the twisted pair cable is used inside the house.
Read Also:
- How to reset the TCP/IP stack on Windows 10
- What is better: Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection for gaming
- Do you need a WiFi card when building a computer
What are the Ethernet models
Among the many ways to “catalog” the different types of Ethernet that have been developed over the past 30 years of using this technology, the most common method is based on the maximum theoretical speed that can be achieved during a file transfer.
10BASE-T
The IEEE 802.3 protocol’s base-level specification is characterized by transmission speeds of 10 megabits (10 million bits) per second. The cables consist of two twisted pairs of telephone lines twisted together, while the RJ-45 connectors were also taken from the telephone line.
Fast Ethernet
Data transmission standards for LAN networks with a theoretical maximum speed of 100 megabits per second. Also, in this case, 100BASE-T is the predominant standard, which is characterized by two twisted pairs and RJ-45 connectors.
Gigabit Ethernet
The evolution of Fast Ethernet, led to a 10-fold increase in speed. As the name implies, Gigabit Ethernet is characterized by transmission speeds of 1 gigabit (1 billion bits) per second, using a 1000BASE-T configuration, copper pairs of telephone wires, and RJ-45 connectors.
2.5GBASE-T, 5GBASE-T and 10GBASE-T with Cat5e, Cat6 and Cat7 cables
However, the evolution of Ethernet cables has allowed technicians and engineers to go beyond the 1-gigabit threshold. Today there are already cables on the market that can reach 10 gigabits per second: this refers to Cat 7 Ethernet cables (also called 10GBASE-T), which can transmit data packets at 1.25 gigabytes per second (1 byte = 8 bits).
However, they are not the only ones that can go beyond the gigabit speed level: with the introduction of the IEEE 802.3bz standard, in fact, significant performance improvements have been made also for Cat 5e and Cat 6 Ethernet cables. The former, also called 2.5GBASE-T, has a maximum data rate of 2.5 gigabits per second; the latter, called 5GBASE-T, can go up to 5 gigabits per second.